Thumb Injuries: The Complete Guide to Diagnosing your Thumb Pain
Texting, typing, gaming … Such activities pervade our lives. Thus, it is not surprising that these activities involving repetitious motions of the thumb have resulted in a number of injuries that take their name from the causal activities, such as gamers’ thumb, skiers’ thumb, technology thumb, blackberry thumb, texting thumb, cubers’ thumb (i.e., Rubik’s Cube – yes, this is a real thing!), stylus finger and trigger finger, to name a few.
More specifically these painful or irritating conditions are repetitive stress injuries that fall under the more scientific categories of tendinitis, tendinosis, carpal tunnel syndrome, osteoarthritis, carpometacarpal joint irritation, collateral ligament injury, etc.
As I alluded to, we use our thumbs frequently throughout the day for technology use and otherwise. Indeed, many jobs require frequent use of the thumbs. For this reason, it is a relief to know that there are thumb stabilizers available that help the thumb to heal while at the same time allowing mobility and range of motion for your hand and thumb.
Scientists say the evolution of the human race can largely be attributed to our ability to make tools, in no small part thanks to our hands and opposed thumb. Whether you are a believer in evolution or not, there is no denying the thumb plays a major role in enabling us to efficiently perform a wide variety of daily not to mention recreational tasks.
For that reason, it is a relief to know that thumb disorders or an injured thumb that disrupt one’s life can usually be treated via conservative methods like splinting and rest. And if that fails, surgery is usually an option for improving if not fully correcting the thumb injury so that you can open a door, lift a baby or swing a bat free of pain.
Learn more about specific Thumb Injuries by clicking on one of the links below, or shop our selection of Thumb Injury Treatment Braces & Thumb Splints. Or, call (866) 712-7808 and one of our friendly product experts will help you find a thumb splint to treat your injury.
Carpal Tunnel Hand & Thumb Injuries
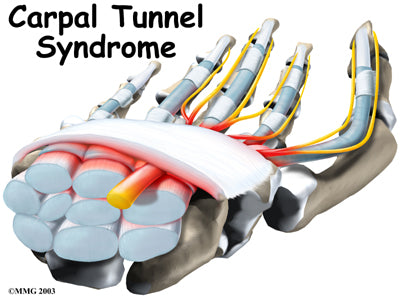
One of the more common hand injuries/thumb injuries, especially among women, is carpal tunnel syndrome. Carpal tunnel thumb injury symptoms include pain, tingling, weakness or numbness in the thumb and possibly the index finger, middle finger and the medial half of the ring finger. These symptoms usually escalate at night and they can radiate all the way up the arm and into the shoulder. Not surprisingly, this can make gripping or pinching objects a difficult task.
These symptoms stem from a pinching of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel on the inner part of the wrist. Why this occurs is not fully understood. It can be simply due to the anatomy of the wrist or due to underlying health issues that cause either inflammation (rheumatoid arthritis, for instance) or nerve damage (like diabetes). Certain activities are also thought to be linked to carpal tunnel, such as repetitive flexing of the wrist (as might be required for assembly line work) or operating vibrating tools.
Treatment of this type of nerve injury to the thumb will depend upon the severity of it. For mild cases, simply resting and icing the wrist should do the trick. If that is not enough, one can splint the wrist for 24 hours a day or simply at night to hold the wrist still, with a brace such as the BraceAbility Thumb Stabilizer.
Taking NSAIDs to reduce the pain and inflammation can also be helpful. In some instances, a doctor may recommend the injection of a corticosteroid, such as cortisone. And if all else fails, surgery to ease pressure on the median nerve may be an option.
Trigger Thumb Injury
Another common thumb injury that is thought to be associated with repetitive gripping motions is trigger finger or trigger thumb. Irritation of the protective sheath that surrounds the tendon of the affected thumb can cause the finger to get stuck in the bent position as one moves the thumb or fingers. When (if) the tendon squeezes through the tendon sheath, it does so with a snapping sensation or sound that brings to mind the release of a trigger.
Forcing the tendon through the sheath increases the irritation and inflammation in the area and over time can lead to the formation of a nodule on the tendon due to the buildup of scar tissue. This makes it even more difficult and painful for the tendon to glide through its sheath.
Treatment for trigger thumb involves resting the thumb and immobilizing it at night, possibly with the help of a trigger thumb brace or splint, such as the non-restrictive Thumb Spica.
Wearing a trigger thumb brace at night is often recommended too as many people curl the digits of the hand up at night. Anti-inflammatory medications can also be helpful for getting the swelling under control.
In some instances, a steroid injection or trigger finger surgery may be needed for achieving relief.
Base of Thumb Injury: de Quervain’s Syndrome
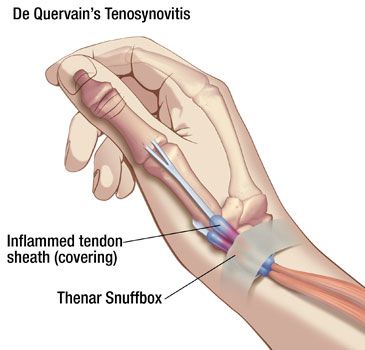
De Quervain’s syndrome refers to a thumb disorder characterized by inflammation of the tendons around the base of the thumb that extends into the wrist, which makes it difficult for them to pass through the tunnel at the side of the wrist as they should. This friction can cause pain around the base of the thumb that may radiate into the thumb or forearm.
Other thumb problems associated with this condition include swelling at the base of the thumb and difficulty and pain when performing actions involving the thumb, especially those requiring pinching or grasping. This pain will typically increase with motion of either the thumb or wrist and the thumb may “stick” when you try to move it. (Watch a video of the Finkelstein’s test for de Quervain’s Syndrome.)
The cause of de Quervain’s syndrome is not well understood, but some generalities have been observed. It is more prominent among women (8 to 10 times more so, in fact) and among those between the ages of 30 and 50. It is also sometimes a side effect of pregnancy.
The inflammation of the tendons is thought to be linked to chronic overuse or repetitive motions of the hand or wrist. Thus, certain activities are irritants of the condition. For instance, de Quervain’s syndrome can be a problematic golf thumb injury or it can make it difficult to play sports involving racquets. Lifting a child over and over can also make the symptoms of this base of thumb disorder worse. A blow to the thumb or the presence of other inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis is also seen as associated with the condition.
Conservative treatment of this thumb tendon injury involves following the steps of RICE, taking anti-inflammatory medications and wearing a splint around the clock for four to six weeks, such as BraceAbility’s Thumb Spica Brace. A steroid injection is also a helpful mode of treatment for some.
If these methods fail to bring relief, surgery to release the thumb tendon covering may be needed, followed by physical therapy.
Thumb Ligament Injuries: Skier's Thumb & Gamekeepers Thumb
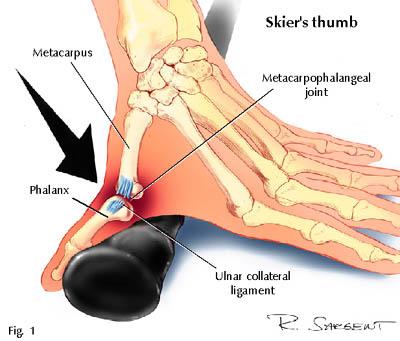
A skier’s thumb injury occurs when one falls against a planted ski pole, which hyperabducts the UCL. A gamekeeper’s thumb occurs over time due to the motion Scottish fowl hunters use with their thumb and index fingers to break the head of a captured bird. This injury, therefore, develops over time from a series of hyperabduction motions that lengthen and thin the UCL. This makes it more difficult to treat. A tear to the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb is associated with several names, including a UCL thumb injury, gamekeeper’s thumb or skier’s thumb. The latter two take their name from activities that can rupture to the UCL ligament.
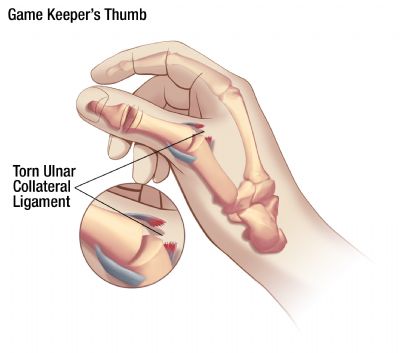
But of course, these are not the only such actions that can result in a valgus force that pulls the thumb away from the hand to tear the UCL. It is actually a relatively common sports injury that can be sustained simply by falling onto an outstretched hand.
UCL injury thumb symptoms include instability of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint at the base of the thumb, along with pain, swelling, weakness and a bruise-like discoloration in the vicinity of the tear. A bump may also form along the edge of the thumb near the palm of the hand. Not surprisingly, these thumb injuries symptoms can make it tough to grasp things between the thumb and index finger.
Treatment for a UCL sprain involves immobilizing the thumb with a spica splint (consider the Gamekeeper’s Thumb Splint Spica or the Skier’s Thumb Brace) or a modified wrist splint for a period of four to six weeks, followed by physical therapy.
But a complete or near total tear of the UCL will typically require surgery to repair. Post-surgical rehabilitation will include wearing a thumb spica cast for four weeks, followed by an immobilizing splint for a few more weeks.
Catchers’ Thumb Injury
A somewhat similar injury known as catchers’ thumb or mallet thumb occurs when a force causes hyperextension of the upper interphalangeal joint of the thumb, such as when a catcher is “thumbed” by a foul ball tipped directly back or when a soccer player is kicked in the tip of his or her thumb. Sometimes, this “super sprain” also pull the extensor tendon away from the bone (this is known as an avulsion), which causes the thumb to stick in a slightly flexed position.
Other symptoms of this thumb joint injury are swelling, pain and trouble performing tasks such as pulling up a zipper, turning a doorknob or tying one’s shoe.
Treatment of this thumb knuckle injury involves splinting the injured joint for a period of eight weeks, followed by thumb splinting at night for two weeks. In some severe cases or in instances where an avulsion occurred, surgery may be necessary to repair the damage.
Volar Plate Injury: Thumb
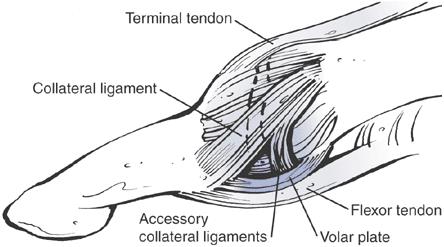
The volar plate of the thumb is a very thick ligament that forms the bottom of the interphalangeal joint and separates the joint space from the tendon sheath. This ligament is responsible for preventing hyperextension. But with enough hyperextension force, the volar plate can be sprained or ruptured.
This injury also often coincides with a collateral ligament tear and it sometimes occurs with enough force to pull a small piece of bone off the finger. This thumb hyperextension injury is sometimes referred to as a “jammed thumb injury.” This might occur when jamming the thumb into the wall, a ball, another player, etc.
While the collateral ligament usually heals without much trouble, scar tissue may form, creating a bulge on one side of the joint. Besides this bulge, symptoms include pain when the finger is at rest and especially when it is moving, swelling or deformity of the finger.
Treatment for such thumb joint problems depends on the extent of the damage. For an injury that can be reduced and that includes no major ligament tears, immobilizing the thumb with a splint may be enough to treat the injury. During this time, it is important to engage in range-of-motion exercises as soon as possible to ward off stiffness.
But in instances where the jam is not reducible or if the injury coincides with a bone avulsion or collateral ligament tear, reconstructive surgery may be needed.
Bowling Thumb Problems
Another sport that can cause damage to the thumb that may not immediately come to mind is bowling. Bowlers’ thumb is an overuse injury that is more common among those who put “spin” on the ball by keeping the thumb in the thumb hole for as long as possible before the release. This pressures the inner part of the thumb, resulting in compression of the ulnar digital nerve.
This can cause tingling at the end of the thumb, numbness, weakness, pain in the inner part of the thumb and in the webbing between the thumb and the index finger. Over time, a nodule may form and permanent nerve damage is possible.
Thus, seeking treatment for such thumb conditions is crucial. This typically involves giving up bowling for a period of time to give the thumb a chance to heal. Splinting the region can also be helpful toward this end.
And when one gets back to bowling, one can use adaptive devices to lessen the risk of bowler’s thumb, such as widening the hole of the ball, changing one’s technique or using protective padding or a splint. Such measures can be used as preventive techniques as well.
But taking an extended break from bowling is not always an option for professional bowlers. In such cases, there are surgical procedures to repair the damage and ease the pain in a relatively quick timeframe.
Thumb Fracture
And of course, a fracture of the thumb can stem from a number of sources of either direct (a fall, a ball pulling the thumb back) or indirect force to the thumb (such as muscle contractions or twisting that might occur in sports like wrestling or hockey). A break can take place anywhere on the distal phalange, which extends from the thumb tip to the knuckle, or the proximal phalange, which is the bone running from the knuckle to the base of the thumb. The more serious breaks that are harder to treat typically occur near the joints of the thumb. Those that occur near the wrist are especially hard to treat.
Someone with a fractured thumb will usually experience severe pain where the break occurred, along with extreme tenderness and a deformed shape of the thumb. Swelling, numbness, coldness, and trouble or (or inability) to move the thumb are other symptoms of a thumb fracture.cur near the joints of the thumb. Those that occur near the wrist are especially hard to treat.
If the break causes minimal bone fragment displacement or it occurs in the middle shaft of the bone, treatment may simply include wearing a spica cast for four to six weeks (possibly longer). But if there is significant bone displacement or a break occurs in other areas, such as a joint, fixation surgery to either internally or externally support the bone so that it can heal may be necessary.
Following surgery, one will likely need to wear a cast or splint for two to six weeks, followed by several months of physical therapy for the hand to regain full range of motion and strength.
Unfortunately, a break greatly increases one’s risk of suffering arthritis down the road. BraceAbility also offers braces like the Thumb Arthritis Treatment Support for easing the pain of arthritis.
Toe Thumb Disorder
If you Google “toe thumb disorder,” you will likely come across a slew of articles on the actress Megan Fox, poking fun at her “one and only flaw.” Toe thumb is slang for a medical condition known as Brachydactyly type D, also known as clubbed thumb syndrome. The scientific name of this condition basically means short digits. This aptly named condition is a genetic one that causes disproportionately short (to varying degrees) fingers or toes. For the thumb, specifically, the distal phalanx usually is shortened and often broader—hence the term “toe thumb.”
The amount of disruption to normal hand use caused by the condition varies. Physical therapy may be helpful for improving the function of the hand. Otherwise, plastic surgery may be another treatment option.
This is by no means an exhaustive list of thumb conditions. Even within each of these categories, there are variations requiring different forms of treatment. Therefore, you should always consult a medical professional before pursuing any line of treatment.