Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
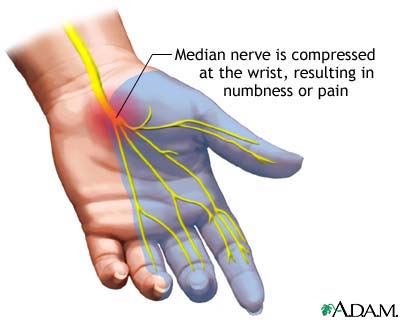
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a very common wrist ailment among U.S. adults. But while this condition is often treated, carpal tunnel itself is not fully understood. A basic definition of carpal tunnel syndrome is that this refers to a number of side effects stemming from pressure on the median nerve. This nerve is responsible for movement and feeling for the thumb-side of the hand (the thumb to the thumb side of the ring finger, as well as the palm).
Now you might be wondering what is a carpal tunnel and how does it play into the carpal tunnel syndrome definition. Well, the median nerve, as well as some tendons, pass through a narrow “carpal tunnel” on the way into the hand. This is where the problematic compression of the median nerve often occurs.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Some are simply born with smaller carpal tunnels, making them more vulnerable to carpal tunnel syndrome. Women are thought to be three times more likely to suffer carpal tunnel syndrome than men due to their relatively smaller carpal tunnels.
In other instances, swelling is the cause of carpal tunnel syndrome. Some believe repetitive motions of the hand/wrist lead to this swelling, whether this is via the use of vibrating tools, typing, assembly line labor or playing an instrument. However, studies have yielded inconclusive results as to this connection.
Following are a few other factors that can lead to painful swelling as well as some other carpal tunnel syndrome causes:
- Wrist injuries, such as a bone fracture or sprain.
- Inflammatory conditions like arthritis (including rheumatoid arthritis) or infection
- A cyst, bone spur or tumor in the wrist.
- Metabolic disorders (e.g., overactive pituitary gland, hypothyroidism)
- Nerve-damaging conditions like diabetes or alcohol abuse
- Fluid retention due to pregnancy, menopause or obesity
What Are the Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The most common symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome are pain, numbness, tingling or weakness in the hand or fingers. Often, people respond to this by “shaking out” the affected hand. In cases of bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome, the discomfort usually begins and is more intense in one’s dominant hand.
Some also experience radiating pain in the forearm with carpal tunnel syndrome. Other signs of carpal tunnel syndrome include a weak grip or coordination issues of the fingers, such as a struggle to complete fine finger movements.
If one fails to treat carpal tunnel syndrome, the condition can result in permanent muscle or nerve damage in the hands. This means the carpal tunnel side effects will also be permanent.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Test
Besides examining the patient’s hand and wrist and asking questions about one’s symptoms, there are two common tests a doctor may do for carpal syndrome diagnosis:
- Tinel’s sign: Tap above median nerve at the wrist. An affirmative test for carpal tunnel syndrome will result in shooting pain in the forearm.
- Phalen’s test: Bend the wrist all the way forward for one minute. Such tests for carpal syndrome will likely bring on the numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand for someone with the condition.
How to Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
As alluded to, addressing the problem is important not only for getting relief for carpal tunnel syndrome but also for preventing permanent damage to the nerve and muscles of the hands and wrists. A carpal tunnel syndrome doctor or another medical professional can tell you what to do with carpal tunnel syndrome to get you on a path to healing. BraceAbility also offers a complete line of wrist injury treatments for CTS and other wrist ailments.
The first line of defense is to rest the hand and wrist for several weeks. This typically involves wearing a wrist splint at night. And if that is not effective, treating carpal tunnel syndrome may require wearing a wrist splint or brace during the day. Our carpal tunnel hand brace is ideal for use both during the day and while sleeping. During this period of rest, one should avoid aggravating activities as much as possible (including sleeping on the hands/wrists).
As noted, a number of underlying conditions can result in carpal tunnel as a side effect. If that is the case, treating the underlying condition will usually eliminate the effects of carpal tunnel. Similarly, carpal tunnel syndrome and pregnancy sometimes go hand-in-hand. But this usually goes away after a mother has given birth. In the meantime, she might find bracing or wrist sleeve helpful for easing carpal tunnel during pregnancy along with the use of carpal tunnel braces for minimizing stress to the wrist.
Other practices to reduce the swelling that aggravates the median nerve include applying a cold compress to the affected area several times a day and to use anti-inflammatory medications.
Once the swelling has gone down, one can engage in physical therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome to help prevent it from flaring up again. Carpal tunnel syndrome statistics show that carpal tunnel yoga can be helpful for treating carpal tunnel. Watch this carpal tunnel syndrome video detailing some simple yoga stretches for the condition.
If these methods do not eliminate the effects of carpal tunnel syndrome, one might try a corticosteroid injection for temporary relief or some alternative methods such as supplements, chiropractic care or carpal tunnel syndrome acupuncture.
In roughly 50% of cases, surgery is needed to resolve severe carpal tunnel syndrome. Recovery from this usually takes months; thus, it is important to consider whether one’s job offers carpal tunnel syndrome workers’ compensation. During this time a wrist immobilizing splint will likely be needed, followed by therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome involving strength and stretching exercises.
How to Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
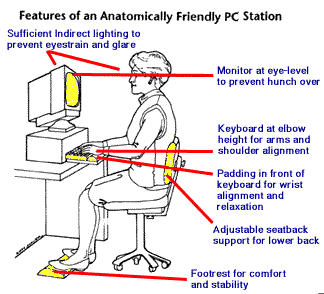
Because of the prevalence of carpal tunnel in today’s society, there are a number of tools one can use to minimize carpal tunnel syndrome median nerve strain. For instance, there are a number of keyboards for carpal tunnel syndrome or one can find a carpal tunnel mouse for work or personal use.
There are also a number of ergonomic practices one can use to avoid a carpal tunnel syndrome disability. See the picture below for some best practices to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome while working on a computer. Or take a look at this New York Times article on carpal tunnel syndrome prevention and the steps and tools workers and workplaces are employing to address the condition.