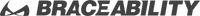Thoracic Back Pain Causes & Symptoms
Where is the Thoracic Back Region?
Your spine consists of 24 bones all stacked up together to make your vertebrate. Those bones are broken up into three different regions: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar.
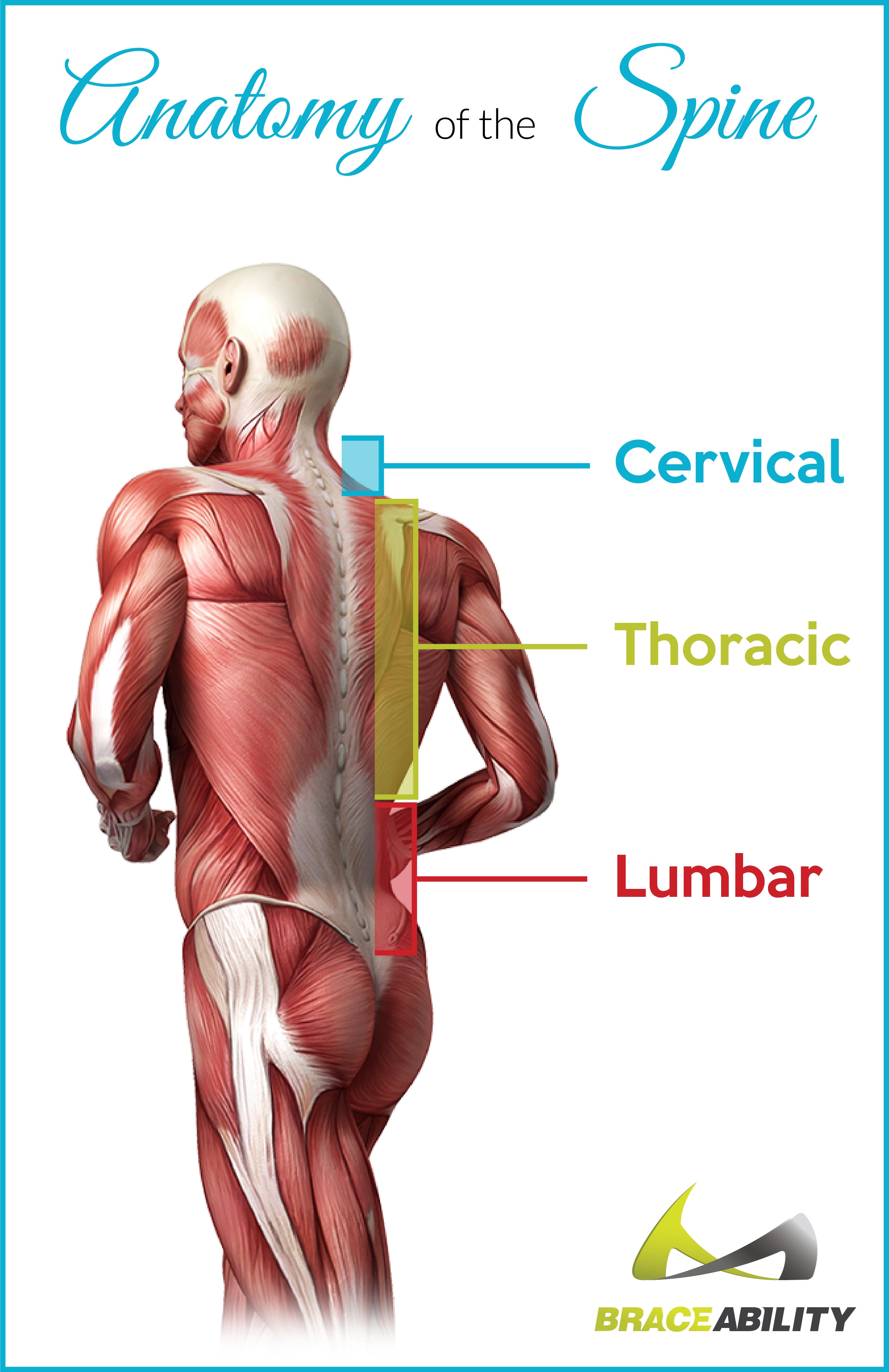
The thoracic region makes up 12 of the 24 bones of the spine. The thoracic spine region refers to the area of the back through which the thoracic spine transverses—roughly the bottom of the neck to the top of the low-back. The thoracic back might also be referred to as the mid- or upper back.
One of the primary roles of this region of the back is to provide stability. Each of the vertebrates in the thoracic region is connected to a rib on both sides and then meet in the front at the sternum. This ultimately builds our rib cage, protecting important organs such as our heart, lungs, liver, etc.
Thoracic Back Pain Symptoms
Besides chronic pain in the thoracic area, located on either side of the spinal cord. There are other symptoms that may arise causing discomfort:- Stiffness
- Limited range of motion
- Muscle spasms
- Thoracic nerve pain symptoms like tingling, numbness, burning, a pins and needles sensation
- Muscle weakness
- Stooped posture
- Referred pain to the ribs, shoulder, arm, fingers, neck or legs
- Changes in bladder or bowel function or incontinence (severe case- seek medical attention immediately)
Are you experiencing pain in your back but don't think it's your thoracic region? Read more about different back problems and injuries to help diagnose your pain!
What is Causing Pain in My Thoracic Region?
Because many causes of thoracic pain have similar symptoms, one should not try to self-diagnose or treat the condition, as this can do more harm than good. Enlist the help of a medical professional to determine what causes thoracic back pain and the appropriate remedy. Following are just a few of the more common causes of thoracic back pain, some of which are related to one another (e.g., osteoporosis often results in compression fractures):- Degenerative disc disease: As you age, you may lose fluid in the discs located in your vertebrae, this reduces the support and flexibility of your spine.
- Arthritis or osteoporosis: Causes your bones to become weak and fragile, occurs when the creation of new bone can't keep up with the removal of old bone.
- Compression fracture: When your bones break or fracture, usually a result of osteoporosis.
- Muscle, fascia, tendon or ligament sprain or strain
-
Poor posture: Poor posture weakens the spine, back, and shoulder muscles and causes them to be stressed and strained. Wear a posture brace during the day to help alleviate chronic neck and back pain.

- Spinal curvature disorders such as kyphosis, lordosis, or scoliosis: Spine curvature disorders are caused by many different underlying factors. Each condition causes the spine to curve abnormally and incorrectly.
- Pinched nerve: Narrowing of the space where spinal nerves leave the spinal cord to go to the rest of the body. This can be caused by herniated discs, degenerated disc disease, or trauma to this specific area.
- Herniated discs: When the inner core of your vertebrate ruptures, pushing it through the crack of the outer piece of the disc in your spine. It can be caused by gender, incorrect lifting techniques, weight, smoking, and genetics.
- Spinal stenosis: Rare, degenerative condition that is a result of the spinal canal being narrowed.
- Diseases such as cancer (and its medications)
What Helps Reduce My Thoracic Back Pain?
There are many different treatment options for thoracic back pain but each is dependent on what condition you have and how severe it is. It's important to speak with your doctor about the best recommendations for your thoracic back pain. Some options may include:- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Bracing
- Hot and cold treatment
- Physical therapy
- Surgery (in some cases)