Back Pain: The Complete Guide to Diagnosing your Back Problems
Learn more about specific back problems and back injuries:
Arthritis in your Back & Spine
Back Muscle Tear, Pull, or Strain
Fractured Vertebrae in your Spine
Sciatica & Pinched Nerve Back Pain
BraceAbility stocks a wide assortment of back treatment braces for most common back disorders.
Back injury statistics make it very evident that back pain is a serious problem for many in America as well as worldwide. Consider the following statistics on back injuries:
- Low-back pain is the leading cause of disability worldwide
- Low-back pain is the most common cause of job-related disability, as well as a leading contributor to missing work (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke).
- Respondents to a National Institute of Health Statistics survey cited low-back pain as the most common type of pain experienced over the past three months (28.4%).
Whether you are suffering from a back injury at work, a sports back hyperextension injury, or hereditary back problems, BraceAbility has an affordable treatment option so you can start feeling better without breaking the bank.
This article takes a look at some of the more common back problems and provides an overview of their symptoms, causes and treatments before getting into some back injury prevention guidelines.
Understanding the Anatomy Behind a Back Injury
A basic understanding of the structure and elements of the spinal cord and back helps can help one get a better grip on a number of back conditions, the definitions of which can be a bit heavy with confusing industry jargon.
The back is made up of a combination of bones, muscles, ligaments, nerves etc. that make up the rear part of the trunk from the neck to the pelvis. At its center is the spinal cord nervous system that is the transporter of the body’s signals for movement and sensation. The spinal cord is encompassed by more than 30 bones (vertebrae) stacked on top of one another that form the spinal column. The spine can be divided into the following regions:
- Cervical spine (neck, C1-C7)
- Thoracic spine (upper back, T1-T12)
- Lumbar spine (lower back, L1-L5)
- Sacrum and coccyx (a fused group of bones at the bottom of the spine)
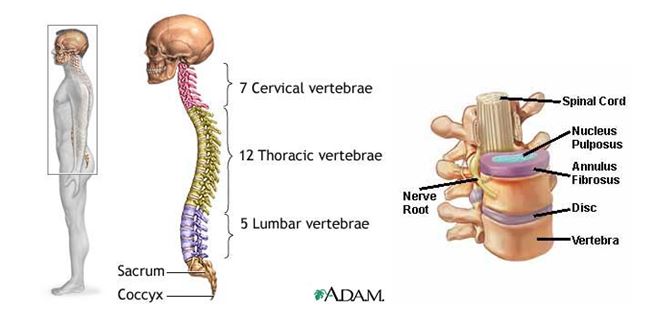
Tiny nerves known as roots exit the spinal canal through spaces between the vertebrae. The space between these vertebrae is maintained by round, spongy discs of cartilage known as intervertebral discs. The spongy quality of these discs allows for flexibility in the spine. Ligaments and tendons also help to hold the vertebrae in place and they attach muscles to the spinal column.
Lower Back Problems
Because the lumbar spine must support the weight of the upper body, not to mention anything else one decides to carry, lumbar spinal injuries are one of the most common back injuries. One of the more common sources of low back is simply straining the muscles or spraining the ligaments of the back. This soft tissue back injury might occur if one lifts a heavy object, engages in a sudden, forceful movement or twists in an unusual manner.
In such cases, treatment for back muscle injuries typically involves giving the back a rest as much as possible, taking anti-inflammatory pain medications and applying back injury ice or heat therapy. Resting the back may involve a period of bed rest (no more than 48 hours) or use of a lumbar back brace.
Exercises and back injury stretches to condition the muscles of the low-back, hips and abdomen and to prevent future back muscle injury or back ligament injury is also incorporated into treatment for back muscle problems or back ligament injury.
Back Disc Problems
Another common lumbar back injury that is also relatively prominent in the neck is degenerative disc disease. This condition can lead to other back spine problems, like a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
Degenerative disc disease is a bit of misnomer in that it actually refers to naturally occurring changes to the spine as one gets older. With the passage of time, the pliable cartilage discs of the spine gradually dry out, diminishing their flexibility and shock absorption qualities. This makes them more prone to injury and pain.
Older discs are also more vulnerable to tears or cracks in the outer part of the disc. If the jelly-like nucleus of the disc is pushed out of the core of the disc, it can cause the disc to bulge, rupture or break into fragments. When the nucleus is pushed out through cracks in the disc, this is known as the herniated disc.
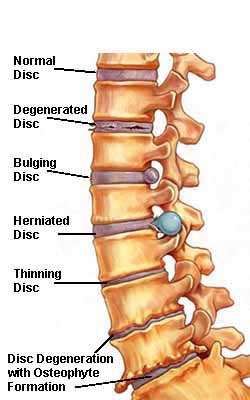
All of this can irritate and cause nerve problems. One might experience pain, numbness, tingling or weakness in the arms or legs, depending upon the location of the disc problem. And this can be a mild back injury with no or few side effects or it can be a severe back injury, such as when it pressures the whole cauda equina (a bundle of spinal roots), necessitating emergency surgery to prevent permanent weakness or paralysis.
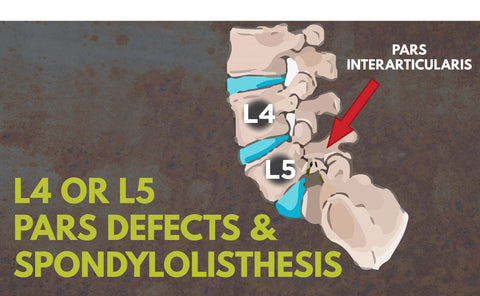
Degenerative back problems with the discs can also lead to conditions such as the back problems sciatica, where the sciatic nerve is pressured, causing pain, tingling, numbness or weakness in the legs, or spinal stenosis, which refers to a narrowing of the open spaces of the canal, which can pressure the spinal cords or nerves. Spondylolisthesis is another condition that can stem from disc degeneration that can cause back nerve problems. This condition is characterized by a forward slipping of the vertebra.
Thankfully, most people can manage these types of back injuries by modifying their activities to avoid irritating movements, in some instances with the help of a supportive low-back or neck brace, taking pain medications and engaging in exercises aimed at minimizing pain from the damaged disc. Over time, this can help the displaced part of the nucleus of the disc to shrink. In rare cases, surgery is necessary to repair a damaged disc, ease pressure on a nerve or to fuse the spine into position. Following surgery, a post-operative back brace may be needed.
Chronic Back Problems
Arthritis is another condition that is sometimes associated with aging. There are a number of forms of this condition that cause painful inflammation and stiffness of the joints, including the spine, with the most common being osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is brought on by the wear and tear of aging that erodes the protective cartilage of the bones. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder. Both of these chronic back conditions are more common among women.
There are a wide variety of medications available for treating the various forms of spinal arthritis. Physical or occupational therapy is also helpful for many. There are also a number of braces and arthritis-friendly tools and aids that can limit painful movements, such as:
- Aids for gripping cans, opening doors, etc.
- Furniture for back problems
- Shoes for arthritis
- Back support braces
- Canes
Losing weight, resting, doing low-impact exercises and applying heat and cold therapy can also be helpful for treating arthritic types of back problems.
Skeletal Back Problems: Scoliosis, Kyphosis, Lordosis
Abnormal curves to the spine are another possible source of back pain as the unusual curve can increase the amount of strain on the vertebrae as well as on the muscles, tendons, ligaments and other tissues that support the spine. Some more common back posture problems include:
- Scoliosis (a sideways curve to the spine, usually either C- or S-shaped)
- Kyphosis (exaggerated forward rounding of the upper spine)
- Lordosis (AKA, swayback; an exaggerated inward curve of the lower spine)
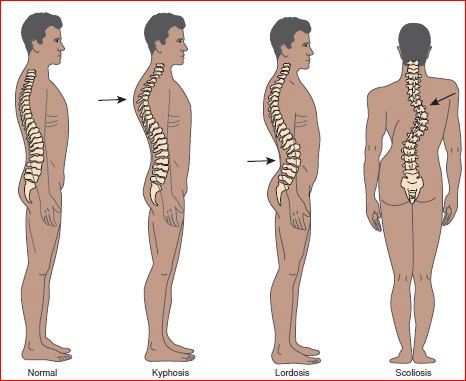
These curved back problems may be due to genetic back disorders that are present since birth, or they can be acquired via poor posture or an injured back.
Other conditions that put pressure on the spine, such as a forward slipping of vertebra known as spondylolisthesis, an infection or a tumor can also cause these different back problems. Or they can sometimes be chalked up to degenerative changes over time, such as osteoarthritis.
On the other end of the age spectrum, posture back problems in teenagers are not uncommon. These may be linked to back problems from backpacks, lowering the head while texting, sports injury or slouching, to name just a few.
Besides the pain in the back and posture abnormalities, other back injury symptoms from kyphosis, scoliosis or lordosis include fatigue in the back or legs and trouble moving in certain ways.
How to fix back problems of this nature depends upon the severity and type of condition. This can range from simply monitoring any progression in the curvature to taking anti-inflammatory pain medications to wearing a posture back brace or undergoing surgery. In many cases, exercise and weight loss (if needed) can be helpful for back injury treatment.
Pediatric bracing is often recommended for scoliosis back problems in children or adolescents as a preventative measure against any worsening of the curve.
Back Problems During Pregnancy
The list of back problems associated with pregnancy can stem from a number of things, including weight gain, an abnormal waddle or compromised posture, to name just of few, all of which can cause lumbar back problems and pain.
Another source of lumbar pain during pregnancy is sacroiliac (SI) joint dysfunction. (This condition can also be brought on by wear or an abnormal gain or it can be a symptom of some other condition, like rheumatoid arthritis.) This sciatic nerve area can also cause back problems after pregnancy. A pregnancy back brace can help one through the final months of pregnancy. During pregnancy, the release of a hormone to improve the laxity of the joints in the interests of childbirth can cause these joints, which are supposed to be relatively immobile, to move more than they typically can or should, causing inflammation and pain. Compounding this problem is the excess weight a woman carries, as this in and of itself can lead to this injury to the back. Here is more information Sacroiliac Joint Pain & Pregnancy.
Besides pain on either side of the spine in the low-back, other signs of back injury to the SI joint can include referred pain in the hip, groin or leg.
A sacroiliac joint belt can help stabilize this area of the back to help one toward back injury recovery. Resting, taking anti-inflammatory pain medication, applying ice and engaging in SI joint exercises can also help girls with back problems. Learn more about SI joint pain treatment.
Traumatic Back Injury & Middle Back Problems
Men are also more prone to certain injuries. (See BraceAbility’s line of back braces for men.) For instance, back injuries statistics signalmen are as much as four times more likely than women to experience a fracture of the vertebrae of the lumbar or thoracic spine. High velocity is typically required to result in this low or middle back injury, such as a car crash, a fall from a height or a sports injury. (See a list of back injuries from fractures, complete with back injury pictures.)
The signs of this acute back injury typically include moderate to severe pain that is heightened by movement. If the spinal cord is also impacted, other signs of such back problems might include numbness, tingling, weakness and possibly dysfunction of the bladder or bowels.
Treatment of a lumbar or thoracic back injury depends upon the pattern of the fracture and what (if any) other injuries exist. Some types of back injury fractures can heal on their own with the help of an immobilizing low back brace or mid-back brace and back injury rehabilitation exercises. In such instances, back injury recovery time is roughly six to 12 weeks, on average.
But unstable fractures from traumatic back injury must be repaired via surgery. Following surgery to repair such severe back problems, a lumbar or thoracic brace will likely be needed, along with back injury rehab to return strength and flexibility to it.
Back Skin Problems
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that affects the skin. The body of someone with psoriasis sends out messages to the skin to speed up the growth cycle of skin cells when there is no such need. These skin conditions can show up on the back, hands, feet, eyelids, mouth, ears etc.—psoriasis can appear anywhere on the body.
This condition is associated with other health conditions like diabetes, depression or heart disease.
There is no cure for psoriasis, but there are some ways to manage its symptoms, which in its most common form include red, raised patches of skin that are topped with a silver or white dead skin cells. There are a variety of medications that can be used to treat the different types of back problems from psoriasis.
Psoriatic arthritis is another condition that unfortunately goes along with psoriasis for roughly a third of sufferers. This condition most often impacts individuals between the ages of 30 and 50 and its onset can be a gradual development of mild symptoms or it can be an acute back injury that comes on suddenly with severe impact.
Psoriatic backbone problems can affect nearly any of the joints of the body and can cause tenderness, pain, swelling or a throbbing sensation in them. Psoriatic arthritis can also cause stiffness of the joints, including those of the spine, as well as a reduced range of motion. Fatigue, changes in one’s nails or redness of the eye can also be symptoms of such problems with back arthritis.
Diagnosing back problems stemming from psoriatic arthritis early on and seeking treatment is important for preventing permanent joint damage. A doctor can recommend a number of medications to control the inflammation and the toll it takes on the joints. Applying ice and heat to the joints is also helpful with bad back problems for some.
Altering the way one goes about certain tasks and taking advantage of arthritic aids or even a back support can make a big difference in how the joints feel.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also a good way to reduce strain on the joints, and regular, low-impact exercises, such as biking or swimming, can be helpful for both one’s muscles and joints.
Prevent Future Back Problems
There are a number of steps one can take to ward off a back injury diagnosis. For one, maintaining a healthy weight and diet are important. Another smart choice is to wear supportive, comfortable, low-heeled shoes; these are the best shoes for people with back problems.
It is also important to use proper lifting techniques and to avoid lifting objects that are too heavy for you to handle. This is especially true in jobs that involve frequent lifting; this is often the culprit for back injuries in nursing or farming, for instance.
Proper form involves lifting with the knees while drawing in the stomach and keeping the head in line with the spine, which should also be straight. It is important to keep the object close to your body while lifting and carrying it and to avoid twisting while lifting.
Proper posture while sitting at work or standing is also important to prevent different types of back injuries. Computer back problems can be avoided by making sure one follows proper desk posture guidelines and by taking advantage of ergonomic aids (keyboards, computer mouse, etc.) if necessary.
Low-impact athletic activities can be helpful for treating and preventing back and spine problems. Keep in mind it is important to always engage in back injury stretches before exercising. Many an athlete has come away from a workout with an injured back muscle.
Smoking is another no-no in terms of spinal health because this habit reduces the blood flow to the lower part of the spine, which can lead to spinal disc degeneration.